 If you experience knee pain on a regular basis, it may be from a number of different causes. For some people, pain may be the result of a knee injury or an ongoing condition. Some people learn to live with the pain by taking pain relievers while others look for more permanent solutions like surgery. There are several serious causes of knee pain which we will look at in turn below.
If you experience knee pain on a regular basis, it may be from a number of different causes. For some people, pain may be the result of a knee injury or an ongoing condition. Some people learn to live with the pain by taking pain relievers while others look for more permanent solutions like surgery. There are several serious causes of knee pain which we will look at in turn below.
Meniscus Tear of the Knee
The meniscus is a c-shaped disc that is rubber and provides cushion to the knee. Each knee has two, one on the outer edge and one on the inner edge which work to keep your knee steady by balancing weight evenly over the knee’s surface. If a meniscus is torn it can prevent your knee from working correctly. Tears in the meniscus are often caused by sudden turns or twisting when the knee is firmly planted, torquing the knee. They can also be caused by heavy lifting or during the play of certain types of sports.
Aging can cause meniscus wear, allowing it to tear more easily. A minor tear can cause pain and a swollen knee which can disappear over two to three weeks. Moderate tears can cause pain either at the center of the knee or on the sides. Over the course of several days the swelling may worsen and the knee may become stiffer. A sharp pain may be felt as the knee is twisted or if you try to bend down. Although the pain may dissipate over several weeks it can quickly return with overuse. If you have a severe tear, pieces of the meniscus that have torn away from the knee can migrate into the joint causing the knee to lock, pop and catch. If your knee locks you might not be able to straighten it out.
Must Read: What are the Treatments for Medial Meniscus Tears?
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the knee is commonly experienced by older people, but younger people can be susceptible too. It can often be a hereditary condition or can be the result of past injuries or infections. This type of arthritis is a result of wear and tear when the cartilage in the joints is worn down. Cartilage does not regenerate, so when it is non-existent bones rub against each other and this can cause pain, stiffness, swelling and a lower range of motion. In some cases bone spurs can form. Being overweight can be another cause of this type of arthritis that can cause knee pain. If a person has a job where they repeatedly place stress on a certain joint this can cause a repetitive stress injury which can be a precursor to osteoarthritis.
Must Read: How to Choose Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Pain Relief
Runner’s Knee – Iliotibial Band Syndrome
This running knee pain injury is common for people who are avid runners. It can happen to any athlete that does an activity involving repetitive knee bending. This could include jumping, biking or walking. This aching pain around the kneecap is caused from a variety of things including overuse, trauma to the knee, foot problems, misalignment and weak thigh muscles.
If you experience pain behind knee, this can be a symptom of runner’s knee. The pain is usually concentrated around the kneecap area right where it meets the thighbone. If you have more pain when you run, kneel, walk or squat this can also be a sign. Knee pain running can be problematic, especially when you want to be able to move around and exercise.
To speed up the healing process you should rest your knee and avoid putting any weight on it. Ice it to bring down the swelling and reduce the pain as much as possible. Wrap your knee in a compression bandage or use a knee brace. You can also elevate your knee and take anti-inflammatory pain medications including Aleve, Advil or Motrin. Stretching and strengthening exercises can also be a good way to reduce pain for the long term. If you have foot issues, it may be time for you to be fitted with the right orthotics for your feet. In some cases, surgery can remove cartilage that has been damages and reposition the kneecap to evenly distribute stress.
Must Read: How to Treat Knee Pain While Running
Medial Collateral Ligament Injury
This is an injury that occurs to the ligament which is located on the inner section of the knee. It is a ligament that holds your tibia in place and it can tear or stretch, causing severe knee pain. A great deal of pressure or stress placed on the outer part of the knee can cause an MCL injury. If you have a tear in your MCL you will usually experience swelling in the knee, and your knee locking when you try to move it. You may also feel pain or tenderness on the inside of the knee joint.
Must Read: Medial Knee Pain Injury – Causes of Inside Knee Pain
Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injury
Although a relatively unusual cause of knee pain, an injury to the Posterior Cruciate Ligament, or PCL, is a possibility that must always be taken very seriously. This is because it can cause both considerable pain and potential long term knee injury. The PCL acts together with the Anterior Cruciate Ligament to keep the whole knee area working together. This is one of the two ligaments that connect the shin bone to the thigh bone. If you experience a tear to the PCL, you may well find yourself feeling unstable on your feet, because of the weakness around the knee area. Pain can also result because of the extra pressure being put on the Anterior Cruciate Ligament, and you will often find the area around the knee swelling up uncomfortably.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament, or ACL, works together with the PCL but is damaged more often. Unfortunately, a tear to this ligament often results in severe and even sometimes disabling levels of pain. This injury is especially likely to occur in people who are highly active; sports players are at particular risk. An X-ray or MRI scan may be needed to determine the precise nature of the problem, but the pain, instability, and sometimes severe swelling that are associated with an ACL injury often result from sudden jarring or deceleration, such as landing awkwardly after a jump. It is very common for an injury to the ACL to be accompanied by another problem in the knee area, such as further ligament damage or cartilage injury. It is sometimes necessary to wear a knee brace during the healing process.
Must Read: Anterior Knee Pain Treatment and Prevention Tips
Baker’s (Popliteal) Cyst
This type of swelling can cause significant pain behind the knee, although in some people it is painless. There are several potential causes, but one of the most common is damage or injury to the tissue behind the knee joint. Sports injuries are, again, a very common cause, especially in contact sports where hits to the knee may be expected. In rare cases, a Baker’s Cyst can be caused by the age-related bone condition, osteoarthritis, or one of a number of similar conditions. This contributes to the cyst being more common in women, and in those of middle age and upward. The swelling itself is filled with fluid, which can look unsightly. Occasionally, the cyst can rupture, which requires medical treatment.
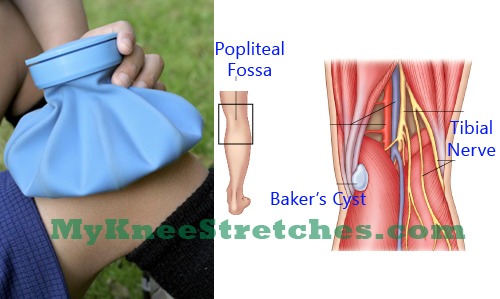
Baker’s Cyst Picture
Must Read: Pain behind Knee Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Sprains & Strains
These are both extremely common causes of a swollen knee, with millions of people suffering from them each year. A sprain is caused when a ligament is torn or badly stretched, while strains are the result of damage to the muscles or tendons. If you play sports a lot, you will probably pick up strains and sprains from time to time. Both types of knee injury result when a joint is forced out of its proper place, for example if you fall awkwardly or are hit on the body. They most commonly result from awkward landings, such as when stretching to slide into a base in baseball or falling onto your knee when landing from a jump in basketball. Long-term overuse of muscles and tendons, or pushing yourself too hard, can also cause chronic strains.
Bursitis
A bursa is a swelling filled with fluid, between the bones and the tendons a little way under the skin, that forms near the joint of the knee. When this becomes inflamed and swollen, that is bursitis. It generally causes knee pain, tenderness, and swelling. You are more likely to get bursitis if you play sports or undertake other physical activities involving repeated movements that cause pressure on the knee joint. It is also common in gardeners, carpet fitters, and other people who spend a lot of time kneeling. Occasionally, bursitis can be caused by complications from long-term conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, or if the initial bursa becomes infected.
Gout Knee
If your knee joint is not only swollen and painful, but also red and warm to the touch, then you may be suffering from gout. This is a type of arthritis which is caused by your body retaining uric acid. This acid is a natural substance from the metabolic process, but is usually dealt with by your body and excreted by the kidneys. When this does not happen, the excess uric acid builds up in the joints in crystal form. This can be extremely painful, as well as leading to difficulty in moving; people with gout also sometimes suffer from a mild fever. Gout is a serious condition that will need to be treated by a health professional to make sure its root cause does not recur.
If you experience chronic knee pain, you should have it diagnosed and treated so that you do not have to deal with the pain on a constant basis. Anything that can be done to reduce pain can make it more comfortable for a person to walk and move with ease.
